

In the case of a round bar, the maximum shear strain is given by: The maximum shear strain occurs on the outer surface. In the case of torsional strain, the member twists by an angle, ϕ, about its axis. Where γ is the shear strain (unitless) and ϕ is the deformed angle in units of radians. In the case of transverse shear strain, the deformation is parallel to the area carrying the force: In the case of normal strain, the deformation is normal to the area carrying the force: Just as the primary types of stress are normal and shear stress, the primary types of strain are normal strain and shear strain. More discussion can be found in the section on bending stresses in beams. In the case of bending stress and torsional stress, the maximum stress occurs at the outer surface. More discussion can be found in the section on shear stresses in beams. In the case of shear stress, the distribution is maximum at the center of the cross section however, the average stress is given by τ = F/A, and this average shear stress is commonly used in stress calculations. In the case of axial stress over a straight section, the stress is distributed uniformly over the entire area. In the equation for torsional stress, T is the torsion, r is the radius, and J is the polar moment of inertia of the cross section. In the equation for bending stress, M is the bending moment, y is the distance between the centroidal axis and the outer surface, and I c is the centroidal moment of inertia of the cross section about the appropriate axis. In the equations for axial stress and transverse shear stress, F is the force and A is the cross-sectional area of the member. Transverse shear stress and torsional stress are both forms of shear stress, τ, since the direction of the force is parallel to the area resisting the force. There are different types of loading which result in different types of stress, as outlined in the table below:Īxial stress and bending stress are both forms of normal stress, σ, since the direction of the force is normal to the area resisting the force. Where L is the deformed length, L 0 is the original undeformed length, and δ is the deformation (the difference between the two).
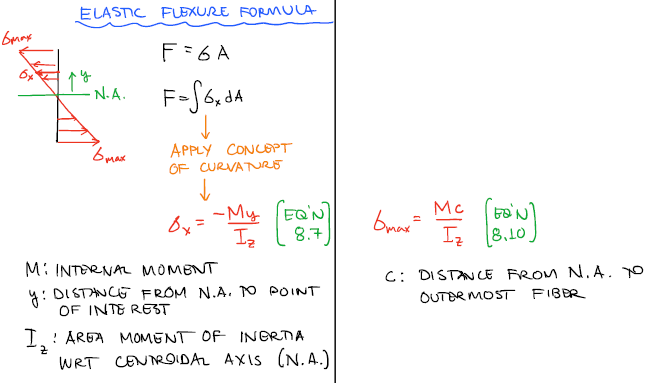
Strain is the ratio of the deformation to the original length of the part: The applied force will cause the structural member to deform by some length, in proportion to its stiffness. Where F is the applied force and A is the cross-sectional area over which the force acts. Stress is the force carried by the member per unit area, and typical units are lbf/in 2 (psi) for US Customary units and N/m 2 (Pa) for SI units: When a force is applied to a structural member, that member will develop both stress and strain as a result of the force.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
